One of my current clients needs to conduct a learning review from a 2-year IT project which, by her own admission, has had its fair share of ups and downs. The project is at its mid-point, so the main customer for the learning is the team itself. They don't have much time to conduct the review (sadly just 90 minutes), so she asked me for some ideas for pre-work for the team. Sometimes you don't have the luxury of a full day to conduct an exhaustive review, so you have to work with what you have and help the team to quickly connect their hearts and minds to the review process. It's the heart bit which interests me here.
When we're under time pressure, we tend to focus on the facts, the timeline, the plan, the process, contract, technology, scope and the deviations. Intellectual recall. In fact, most project review documents contain little more than this kind of intellectual recall. It usually takes a bit longer to get a team to talk about how they felt, and to draw out some the more people-oriented learning - let's call that a kind of "emotional recall".
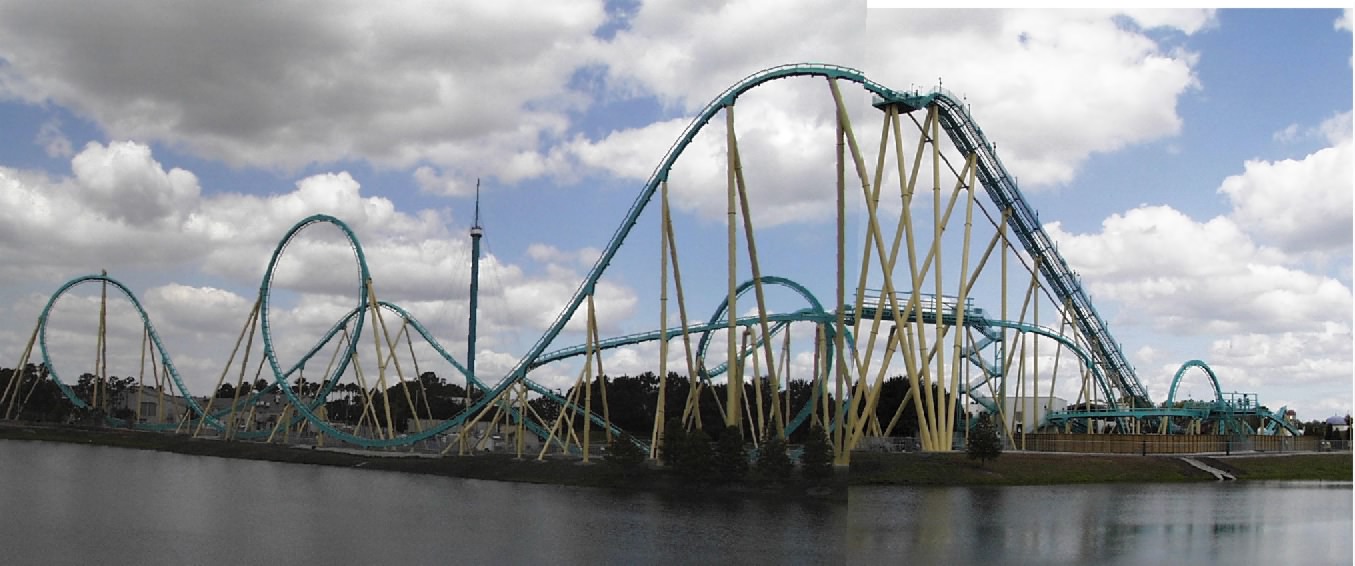
I combined some ideas from Retrospects, After Action Reviews, Baton-passing and Future Backwards (Heaven and Hell) exercises into this approach. Enjoy the ride!
Part 1 - the pre-work:
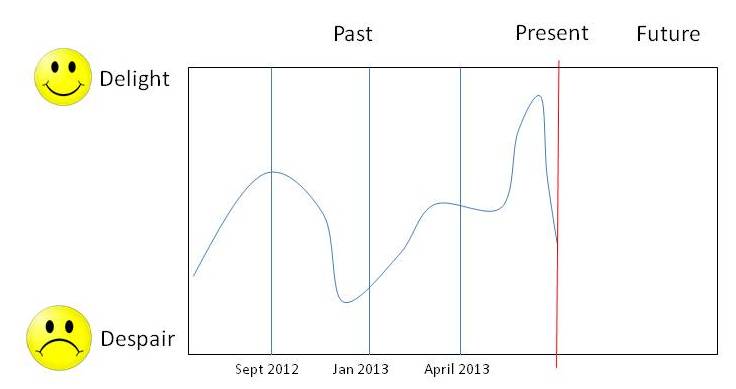
Before the meeting, ask each member of the team to think back over the project timeline and to focus on their emotions at each stage. You can provide them with a template like this, with key dates or milestones marked to give a sense of orientation.
1. Ask them to sketch out their own "emotional rollercoaster", paying attention to the highs and lows.
2. For the high spots, write down what went well, and why you think it went well.
3. Do the same for the low spots. What was difficult, and why do you think that was?
4. How do you think the rollercoaster is most likely to continue? Draw the continuing journey. Bring this to the meeting with your notes on the reasons for the highs and lows.
Part 2 - during the meeting.
Sharing the Past and Present.
- Collectively, in the meeting, create a large version of the rollercoaster timeline on the wall.
- Each participant draws their journey up to the present day, pausing to describe the lows and highs, and the reasons for these. A facilitator should probe these reasons using the "5-whys" technique to get to the underlying reason.
- For each high and low, ask the group to express the reason as a recommendation - something that someone else should do to repeat the delight, or avoid the despair - or an action which should be taken in order to change a process such that the good practice becomes embedded.
- Capture these recommendations on post-its and place on the rollercoaster.
- Repeat for each member of the project team (towards the end, they can "pass" if someone has already identified a high or low. )
- This should create a shared view of the past, and "how we got to where we are today", with some useful recommendations captured. Consider who you might share these with beyond the team.
Creating the Future together.
- Now ask each member to sketch how they think the project will go from now to the end date. You will probably get a range of options!
- Focus on the best projected outcome and ask "based on all we've learned to date, what actions could we take to make this happen, rather than the less positive options?". You can take feedback from the entire group, or get them to discuss in pairs or sub-groups first.
- Capture these actions (with names!).
Thank you ladies and gentlemen, this is the end of the ride. Please be sure to collect your belongings as you leave and don't forget to check your photo on the way out.







 Billy Ray is a homeless Kansas man who received an unexpected donation when passer-by Sarah Darling accidentally put her engagement ring into his collecting cup. Despite being offered $4000 for the ring by a jeweller, he kept the ring, and returned it to her when, panic-stricken, she came back the following day. Sarah gave him all the cash she had in her purse as a reward, and as they told their good-luck story to friends - who then told their friends - her finance decided to put up a website to collect donations for Billy Ray. So far, $151,000 have been donated as the story has gone viral around the world. Billy Ray plans to use the money to move to Houston to be near his family. You can see the whole story
Billy Ray is a homeless Kansas man who received an unexpected donation when passer-by Sarah Darling accidentally put her engagement ring into his collecting cup. Despite being offered $4000 for the ring by a jeweller, he kept the ring, and returned it to her when, panic-stricken, she came back the following day. Sarah gave him all the cash she had in her purse as a reward, and as they told their good-luck story to friends - who then told their friends - her finance decided to put up a website to collect donations for Billy Ray. So far, $151,000 have been donated as the story has gone viral around the world. Billy Ray plans to use the money to move to Houston to be near his family. You can see the whole story 
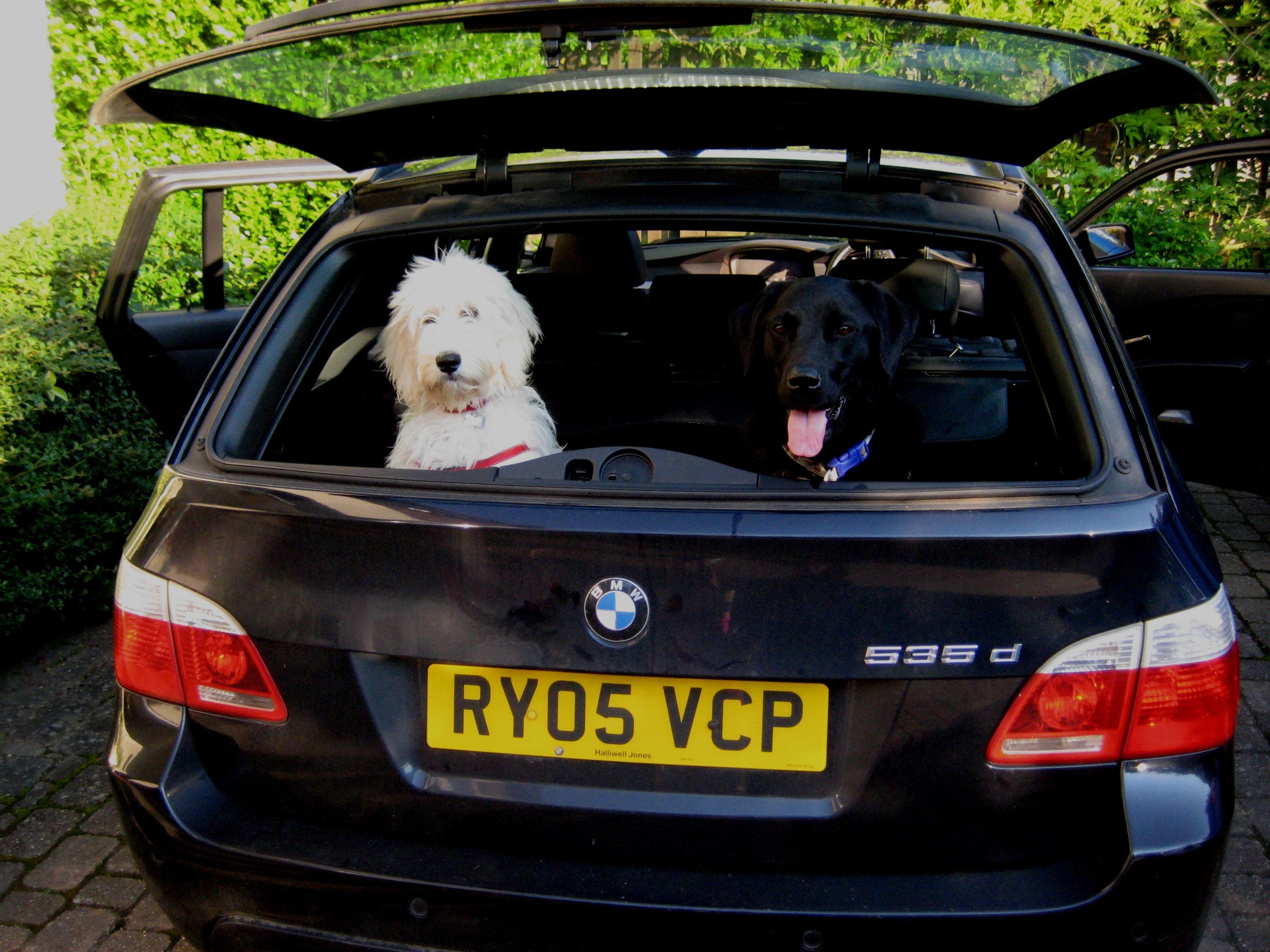 Our BMW is nearly 8 years old now. It’s been brilliant, and it’s had to put up with a lot from a growing family, and now a dog with an affinity for mud and water.
Our BMW is nearly 8 years old now. It’s been brilliant, and it’s had to put up with a lot from a growing family, and now a dog with an affinity for mud and water.